Archaeologists from the University of Chile and the Millennium Nucleus Ocean Heritage and Culture (OHC), have discovered a submerged prehistoric site with remains of an extinct species.
The discovery was made in the Quintero Bay on the central Chilean coast, where the researchers have been excavating a site designated GNL Quintero 1 (GNLQ1).
During the last Ice Age (approximately 24,000 to 17,000-years-ago), the marine space that Quintero Bay occupies was a large esplanade of wetlands which stretched several miles from the current coastline. The esplanade was home to various extinct fauna such as paleolamas, mylodones, American horses and deer, as well as species of rodents, foxes and coypus.
With the thawing of the ice sheets, a rise in sea levels caused the esplanade to become submerged, providing the only known end-of-Pleistocene submerged site on the Pacific coast of South America.
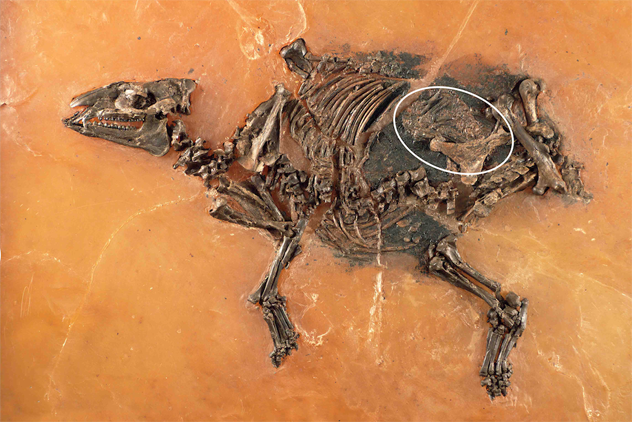
A study of GNLQ1 by archaeologists and palaeontologists have uncovered deposits of camelidae, cervidae, equidae, mylodontidae, xenarthra, canidae, myocastorinae, and octodontidae, in addition to numerous remains of mylodon, all of which are similar to types of animals found at sites of Paleoindian hunter-gatherers in similar environments in central Chile.
The underwater field work consisted of an excavation by strata, vacuuming the sediments that were cleared to later recover the faunal assemblages in blocks, together with the sediment that contained skeletal remains.
“We have also recovered medium-sized species such as foxes, a large number of microfauna made up of various species of rodents, very small marsupials and even remains of reptiles”, said Professor Isabel Cartajena, Director of the OHC and an academic at the Department of Anthropology at the University of Chile.

In total, the researchers have found more than 7,000 skeletal remains, of which 8 have been identified as extinct fauna and dozens of individuals corresponding to minor fauna. “The high taxonomic diversity is especially striking, since the group is made up of more than fifteen species,” Cartajena emphasises.
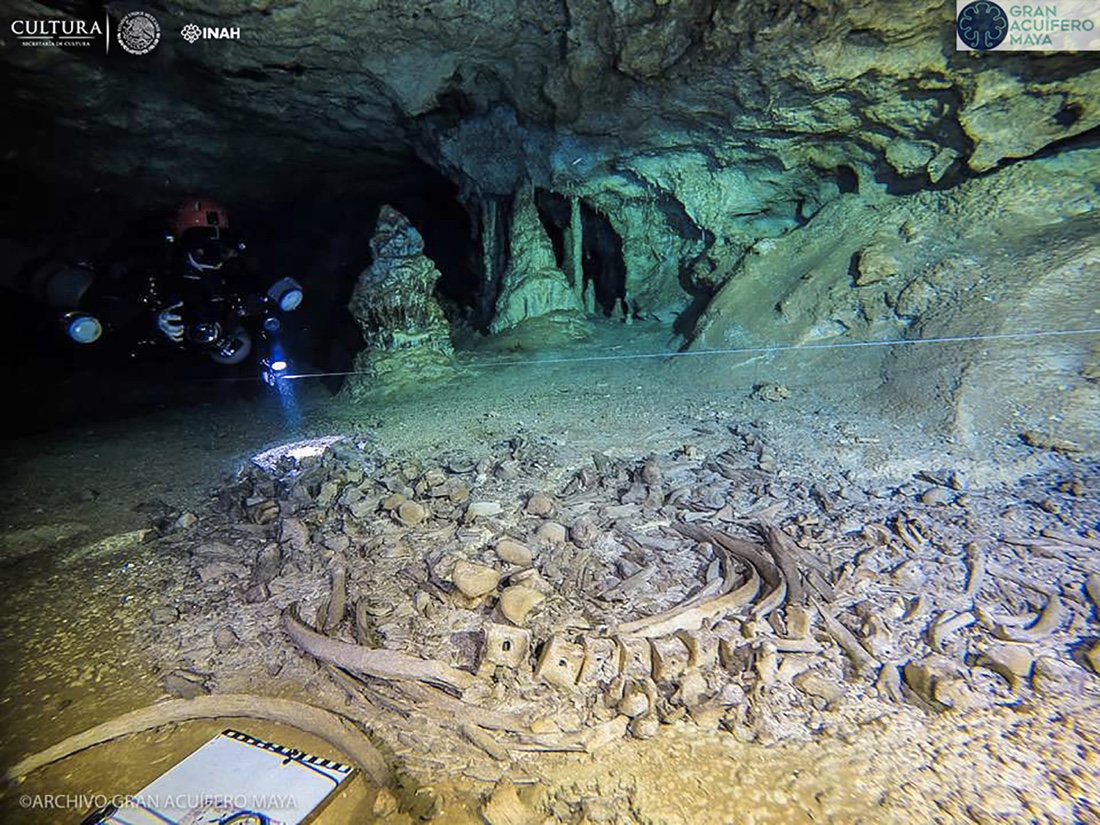

“Until now, the GNLQ1 site has not reported cultural evidence supporting the presence of early human groups. However, this site demonstrates the existence of a landscape available for the occupation and mobility of extinct fauna and early human groups along the Pacific coast of South America”, comments the director of OHC and academic at the Faculty of Social Sciences of the U of Chile.
Src: heritagedaily.com








